What Is Cross-chain and Why It Is Important?

In this article, we will look at the difference between blockchains and the technologies that allow you to transfer tokens between different blockchains. I won’t go into technical details, my task is to explain the basic principle of how it works and help you get started using these tools.
What is cross-chain?
Let’s start by explaining what blockchain and cross-chain are. Blockchain is literally a chain of blocks — a network in which one block of transactions sequentially follows another and the network is supported by miners/nodes.
The first blockchain is the Bitcoin blockchain, since its launch many other blockchains have been created. An important milestone in the development of blockchain technology was the launch of the Ethereum network with the support for smart contracts. Smart contracts are the technology empowering all the DEX, DeFi, NFT, GameFi, Multichain, and Cross-chain projects.
Cross-chain is a tool that connects different blockchains, allowing you to transfer assets between them.
How cross-chain works
Here we come to the key point — how does cross-chain interoperability works?
Cross-chain interoperability is possible for any blockchain that supports smart contracts. For example, the most popular Ethereum token standard is ERC20, BSC is BEP20, HECO is HRC20, ThunderCore is TT20 and most of the blockchains are using the Solidity programming language.
Users can transfer assets between different networks and developers can build multichain DApps because blockchains support common development standards.
Each blockchain works separately and independently from the other, and cross-chain bridges empower users and projects by unifying these ecosystems.
If blockchains work independently, how do tokens transfer between them? Well… technically there is no transfer between the networks, just the blockchains exchanging asset status. Does that sound complicated? Let’s break it down in detail using the example of transferring BNB from the BSC network to the ThunderCore network.
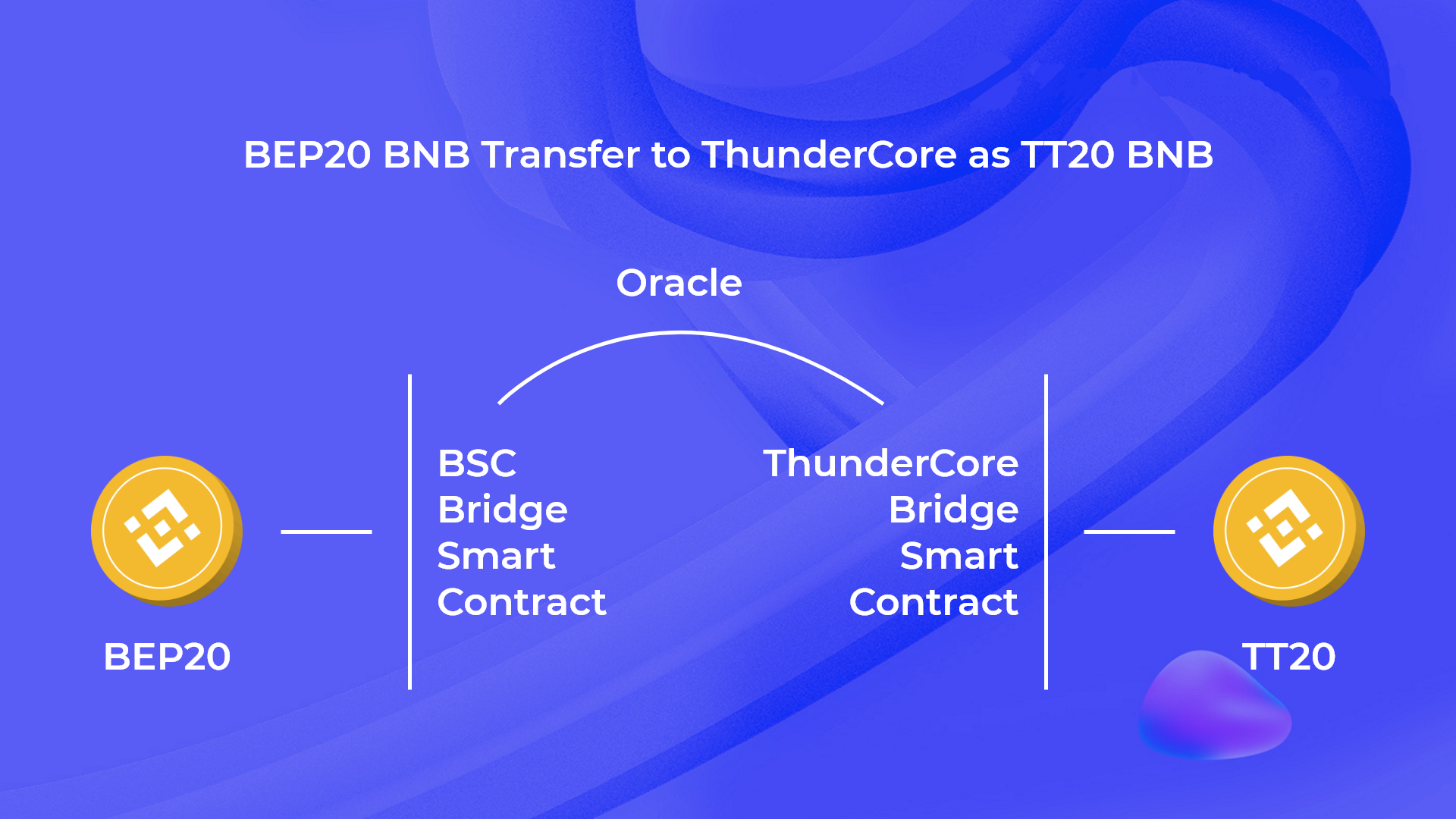
Let’s say you’ve decided to transfer BNB from the BSC network to the ThunderCore network: you use the cross-chain bridge, choose the networks, specify the amount of BNB, and enter the recipient’s wallet address.
After the transfer, the smart contract of the cross-chain bridge locks your BNB in the BSC network, then the information about the number of locked BNB and the recipient’s wallet address via the bridge’s oracle transmits to the ThunderCore network. After that, the bridge’s smart contract in the ThunderCore network unlocks the same amount of BNB and sends them to the specified wallet in the ThunderCore network. All of this happens automatically.
Oracle is a tool for transferring data to the blockchain. Since the blockchain itself is a closed ecosystem, information from the outside does not flow directly into it, so oracle projects are important for the correct operation of smart contracts such as cross-chain transfers.
Why is cross-chain important?
Being able to transfer assets between chains greatly increases the value of these assets because they can be used in more scenarios and provide more yield.
For example, you can transfer BNB, BUSD, ETH, WBTC, USDT, USDC, HT, and HUSD from Ethereum, BSC, and HECO to ThunderCore and use them in various DApps in the ThunderCore ecosystem:
- You can hold USDT in ThunderCore Hub and simply for that earn 5% APR without lockups and limits. You can also become a liquidity provider for these assets in TTSwap and earn from swap fees.
- You can use BUSD in TT Farm to earn high APYs from various animals.
- You can lend and borrow assets in RAM Protocol and earn interest.
- You can transfer TT from ThunderCore to Ethereum or BSC.
TT being listed on Uniswap as an ERC20 wrapped token and on PancakeSwap as a BEP20 wrapped token greatly increases its market exposure because these DEXes are more popular than most of the centralized exchanges. Such listings also introduce TT to a larger base of crypto-investors.
The current blockchain trend is compatibility. In order to be more popular, you must be integrated with other popular chains. With the boom of DeFi, you can’t build closed ecosystems anymore. CEXes are still the popular option for trading, but DEXes like PancakeSwap, Uniswap, and others are already bigger than many centralized exchanges. A wide range of DeFi protocols offers greater earnings than most of the usual banking and CEX solutions.
Popular DeFi protocols are multichain. They offer great products on several chains to allow their users to benefit from these ecosystems. Cross-chain and multichain are the big trends in the blockchain industry because it creates an internet of blockchains where most of the networks can be compatible with each other in a truly decentralized way without intermediaries.
ThunderCore has achieved a lot in cross-chain compatibility, making it one of the most user-friendly blockchains for both users and developers, and with the upcoming launch of the second phase of the Iris hard fork, it will become even more accessible for easy DApp portability from BSC, Ethereum, HECO, and others.

